Run the ssh-copy-id script by specifying the user and IP address of the server that you want to install the key on, like this: ssh-copy-id demo @ SERVERIPADDRESS After providing your password at the prompt, your public key will be added to the remote user’s.ssh/authorizedkeys file. Install an OpenSSH compatible SSH client if one is not already present. Install Visual Studio Code or Visual Studio Code Insiders. Install the Remote Development extension pack. If you do not have an SSH host set up, follow the directions for Linux, Windows 10 / Server (1803+), or macOS SSH host or create a VM on Azure. Cerberus FTP Server fully supports TLSv1/SSLv3 encryption over FTP (FTPS), HTTPS, and SSH SFTP. To enable FTPS, HTTPS, and SSH SFTP support, a digital certificate must be generated for the server. This digital certificate contains the necessary security data to allow the server to establish encrypted connections with clients. Create the key pair. On the computer (such as client1.cyberciti.biz), generate a key pair for the.
If you are a Linux user then you should know that one of the most important ways of using Linux is via SSH. You can do everything from installing software to configuring Linux as a web server with the help of remote access command line tool. SSH can save time, make you more productive, and help you unlock the power of your Linux distro.
But do you know how to Set Up SSH on Linux on both the client and server sides? If you don’t then here in this article of MAZHD, we will show you how to install and configure SSH software at both ends and remotely control your Linux computer.

Related: How to Test or Change Refresh Rate on Monitor Windows 10?
What Is SSH?
Simply SSH stands for Secure Shell and allows you to remotely control a Linux computer or server from another device. SSH (Secure Shell) works across local area networks and the internet. By saying that we meaning that it can be used to manage a Linux-powered media server in your house, or a Linux web server on a different continent.
SSH lets you use the terminal but doesn’t give you access to the remote computer’s desktop environment. When it’s connected to the remote computer you can use it as if it was right in front of you. Just be sure to have root access.
Remember that to use SSH, you’ll need to ensure that the remote computer (server) has SSH set up. Additionally, your local device (the client) will need an SSH app installing.
Client-Side Installation
It is easy and simple to install and set up SSH on a client. And may be there is no need to use any additional software.
Follow the steps below:

- Linux users should find a SSH client built into the terminal
- macOS computers also have SSH preinstalled in the terminal
- Windows PCs will need to use the PowerShell command line tool, or install PuTTY
- To connect to Linux over SSH from iPhone and iPad try iTerminal ($4.99)
- If you’re using Android for SSH, try JuiceSSH (Free)
SSH not installed on your Linux system? Add by updating packages and upgrading, then installing:
If you have recently switched to a Linux desktop but you used SSH on Windows then you might miss the PuTTY desktop SSH app with its easy mouse interface. But don’t worry, it can be installed on a Linux desktop:
When you are done installing SSH client software, you’re ready to set up a connection to your remote computer or server.
Remember that for all desktop and mobile clients, all you need is an IP address or host name, and appropriate login details. While the look of the apps may differ, and the port name may need entering manually, SSH clients are mostly indistinguishable.
Server-Side Installation and Configuration
Install the server-side software to host your SSH connection before establishing a connection. This requires someone to be present to install or enable SSH. You might already be present to do this—otherwise, a colleague or support engineer at the server end will set up SSH.
Remember that if you’re using a web hosting package, SSH should be enabled by default. Speak to your web host to set up SSH if not.

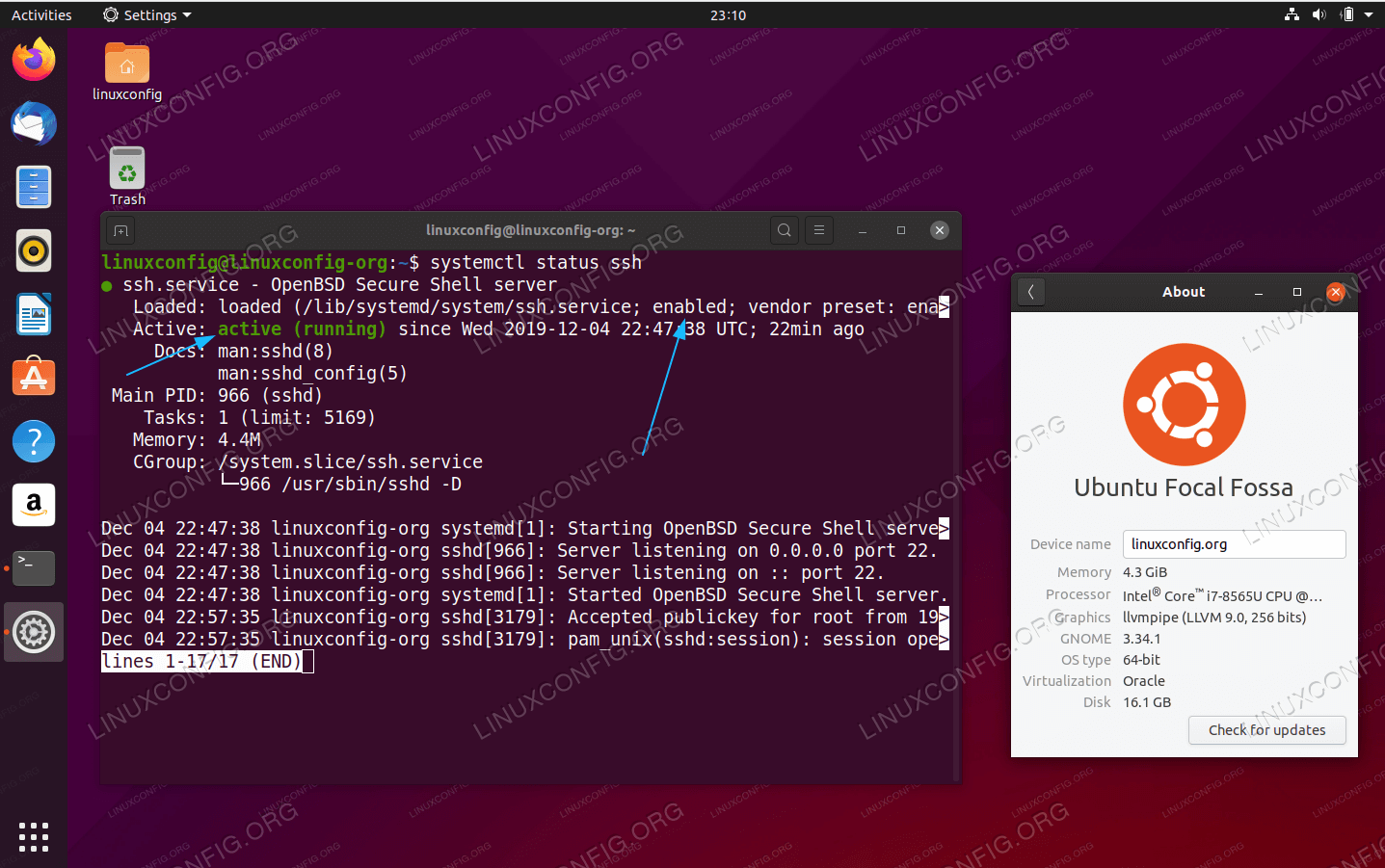
If SSH is not enabled on the remote computer or server, install it with
Check this worked with
The command should illicit a response of “active.”
In some cases the Ubuntu firewall ufw may block SSH. To ensure this doesn’t happen, use
In some cases you’ll need to also enable SSH on the remote device. This is a security precaution that can be tweaked using
Other options are available (stop, start, and disable) for configuring the SSH service.
Determine IP Address
You have to find IP address of the machine in order to connect to the remote device over SSH. mostly it’s done via two easy ways.
- Run a terminal command
- Check the router
To display the IP address of the remote system, logon and run
This will return the device’s IP address, so take a note of it. On older Linux versions ifconfig may provide better results.
You can also check your router to see connected devices. The Linux PC or server will be listed, typically by operating system or device name. This should make it simple to identify.
To display the public IP address, login to the server and open whatsmyip.org.
It’s better to use the IP address which is suitable for the connection. Use the local IP address if the device is on the same network as the client. And use the public IP address for connections across the internet. If the computer is located on a different network, make sure that port 22 is forwarded to the computer.
Related: How to Optimize Windows 10 for Performance & Gaming?
Connecting to Linux via SSH
In addition to correct IP address, you should also have a username and password to gain access to the remote machine.
For command line SSH tools, use
Remember to replace username with the actual username and REMOTE.IP.ADDRESS.HERE with the remote device’s IP address. Then hit Enter, and you’ll be prompted for the password.
With a correct password, you’ll get a functioning terminal prompt—you’re now logged into the remote computer.
Using a desktop SSH client like PuTTY?
How To Setup Ssh Server In Windows 7
After doing the steps above, input the Host Name or IP address, select the SSH connection type, then Open. When prompted for your username and password, enter them in the command line window to complete the connection and gain remote access.
Can’t Connect? Troubleshoot Your SSH Set Up
If you are done the process above and you still can’t connect or you are having SSH connection issues, these are the possible causes:
- SSH software isn’t installed on either computer
- Your username or password is incorrect
- The IP address is wrong
- A firewall is blocking the connection, or port 22 is not being forwarded
Double-check each point and you should be able to connect. If not, the problem might be more complex.
Using Linux Remotely With SSH
Moreover, SSH is a useful tool for managing one or more Linux computers.
With the help of SSH you can work on any machine from just one system. You can input almost any Linux terminal command over SSH.
Key examples include:
- Update: sudo apt update && sudo apt upgrade
- Check status: uptime
- Running processes: ps
- Running processes by CPU: top
Setup SSH and Make Linux More Powerful
With the help of SSH, Linux becomes considerably more flexible and powerful. You can literally remotely access a computer using a smartphone thanks to SSH.
Debian Setup Ssh Server
Moreover, if SSH is set up correctly, with client and server-side software enabled and configured, remote command line access is possible.
Related Searches:
- ssh command example
- ssh server linux
- putty
- ssh command windows
- SSH on Linux
- how to connect from one server to another server in linux
- ssh commands
- ssh port
- putty
- ssh command with password
- “ssh -l” command
- putty
- ssh configuration in linux
- ssh connection refused
- putty
- ssh connection refused
- ssh example
- setting up ssh cisco
- ssh meaning
- ssh-keygen linux
- how to set up ssh mac
- ssh tutorial
- ssh tutorial pdf
- set up ssh windows
- SSH on Linux
- ssh server
- putty
- ssh tutorial ubuntu
- SSH on Linux
- set up ssh linux
- SSH on Linux
- ssh linux
If you have any problem setting up SSH on Linux or you have any question regarding of this title just leave a comment down below.
Source:makeuseof
Related
This tutorial walks you through creating and connecting to a virtual machine (VM) on Azure using the Visual Studio Code Remote - SSH extension. You'll create a Node.js Express web app to show how you can edit and debug on a remote machine with VS Code just like you could if the source code was local.
Note: Your Linux VM can be hosted anywhere - on your local host, on premise, in Azure, or in any other cloud, as long as the chosen Linux distribution meets these prerequisites.
Prerequisites
To get started, you need to have done the following steps:
- Install an OpenSSH compatible SSH client (PuTTY is not supported).
- Install Visual Studio Code.
- Have an Azure subscription (If you don't have an Azure subscription, create a free account before you begin).
Install the extension
The Remote - SSH extension is used to connect to SSH hosts.
Remote - SSH
With the Remote - SSH extension installed, you will see a new Status bar item at the far left.
The Remote Status bar item can quickly show you in which context VS Code is running (local or remote) and clicking on the item will bring up the Remote - SSH commands.
Create a virtual machine
If you don't have an existing Linux virtual machine, you can create a new VM through the Azure portal. In the Azure portal, search for 'Virtual Machines', and choose Add. From there, you can select your Azure subscription and create a new resource group, if you don't already have one.
Note: In this tutorial, we are using Azure, but your Linux VM can be hosted anywhere, as long as the Linux distribution meets these prerequisites.
Now you can specify details of your VM, such as the name, the size, and the base image. Choose Ubuntu Server 18.04 LTS for this example, but you can choose recent versions of other Linux distros and look at VS Code's supported SSH servers.
Set up SSH
There are several authentication methods into a VM, including an SSH public/private key pair or a username and password. We strongly recommend using key-based authentication (if you use a username/password, you'll be prompted to enter your credentials more than once by the extension). If you're on Windows and have already created keys using PuttyGen, you can reuse them.
Create an SSH key
If you don't have an SSH key pair, open a bash shell or the command line and type in:
This will generate the SSH key. Press Enter at the following prompt to save the key in the default location (under your user directory as a folder named .ssh).
You will then be prompted to enter a secure passphrase, but you can leave that blank. You should now have a id_rsa.pub file which contains your new public SSH key.
Add SSH key to your VM
In the previous step, you generated an SSH key pair. Select Use existing public key in the dropdown for SSH public key source so that you can use the public key you just generated. Take the public key and paste it into your VM setup, by copying the entire contents of the id_rsa.pub in the SSH public key. You also want to allow your VM to accept inbound SSH traffic by selecting Allow selected ports and choosing SSH (22) from the Select inbound ports dropdown list.
Auto shutdown
A cool feature of using Azure VMs is the ability to enable auto shutdown (because let's face it, we all forget to turn off our VMs…). If you go to the Management tab, you can set the time you want to shut down the VM daily.
Select Review and Create, then Create, and Azure will deploy your VM for you!
Once the deployment is finished (it may take several minutes), go to the new resource view for your virtual machine.
Connect using SSH
Now that you've created an SSH host, let's connect to it!
You'll have noticed an indicator on the bottom-left corner of the Status bar. This indicator tells you in which context VS Code is running (local or remote). Click on the indicator to bring up a list of Remote extension commands.
Choose the Remote-SSH: Connect to Host command and connect to the host by entering connection information for your VM in the following format: user@hostname.
The user is the username you set when adding the SSH public key to your VM. For the hostname, go back to the Azure portal and in the Overview pane of the VM you created, copy the Public IP address.
Before connecting in Remote - SSH, you can verify you're able to connect to your VM via a command prompt using ssh user@hostname.
Note: If you run into an error ssh: connect to host <host ip> port 22: Connection timed out, you may need to delete NRMS-Rule-106 from the Networking tab of your VM:
Set the user and hostname in the connection information text box.
Openssh For Windows 10
VS Code will now open a new window (instance). You'll then see a notification that the 'VS Code Server' is initializing on the SSH Host. Once the VS Code Server is installed on the remote host, it can run extensions and talk to your local instance of VS Code.
You'll know you're connected to your VM by looking at the indicator in the Status bar. It shows the hostname of your VM.
The Remote - SSH extension also contributes a new icon on your Activity bar, and clicking on it will open the Remote explorer. From the dropdown, select SSH Targets, where you can configure your SSH connections. For instance, you can save the hosts you connect to the most and access them from here instead of entering the user and hostname.
Once you're connected to your SSH host, you can interact with files and open folders on the remote machine. If you open the integrated terminal (⌃` (Windows, Linux Ctrl+`)), you'll see you're working inside a bash shell while you're on Windows.
You can use the bash shell to browse the file system on the VM. You can also browse and open folders on the remote home directory with File > Open Folder.
Create your Node.js application
In this step, you will create a simple Node.js application. You will use an application generator to quickly scaffold out the application from a terminal.
Install Node.js and npm
From the integrated terminal (⌃` (Windows, Linux Ctrl+`)), update the packages in your Linux VM, then install Node.js, which includes npm, the Node.js package manager.
You can verify the installations by running:
Install the Express generator
Express is a popular framework for building and running Node.js applications. You can scaffold (create) a new Express application using the Express Generator tool. The Express Generator is shipped as an npm module and installed by using the npm command-line tool npm.
The -g switch installs the Express Generator globally on your machine so that you can run it from anywhere.
Create a new application
You can now create a new Express application called myExpressApp by running:
The --view pug parameters tell the generator to use the pug template engine.
To install all of the application's dependencies, go to the new folder and run npm install.
Run the application
Last, let's ensure that the application runs. From the terminal, start the application using the npm start command to start the server.
The Express app by default runs on http://localhost:3000. You won't see anything in your local browser on localhost:3000 because the web app is running on your virtual machine.
Port forwarding
To be able to browse to the web app on your local machine, you can leverage another feature called Port forwarding.
To be able to access a port on the remote machine that may not be publicly exposed, you need to establish a connection or a tunnel between a port on your local machine and the server. With the app still running, open the SSH Explorer and find the Forwarded Ports view. Click on the Forward a port link and indicate that you want to forward port 3000:
Name the connection 'browser':
Setup Ssh Server Linux Mint
The server will now forward traffic on port 3000 to your local machine. When you browse to http://localhost:3000, you see the running web app.
Edit and debug
From the Visual Studio Code File Explorer (⇧⌘E (Windows, Linux Ctrl+Shift+E)), navigate to your new myExpressApp folder and double-click the app.js file to open it in the editor.
IntelliSense
You have syntax highlighting for the JavaScript file as well as IntelliSense with hovers, just like you would see if the source code was on your local machine.
When you start typing, you'll get smart completions for the object methods and properties.

Debugging
Set a breakpoint on line 10 of app.js by clicking in the gutter to the left of the line number or by putting the cursor on the line and pressing F9. The breakpoint will be displayed as a red circle.
Now, press F5 to run your application. If you are asked how to run the application, choose Node.js.
Setup Ssh Server On Windows
The app will start, and you'll hit the breakpoint. You can inspect variables, create watches, and navigate the call stack.
Press F10 to step or F5 again to finish your debugging session.
You get the full development experience of Visual Studio Code connected over SSH.
Ending your SSH connection
You can end your session over SSH and go back to running VS Code locally with File > Close Remote Connection.
Congratulations!
Congratulations, you've successfully completed this tutorial!
Next, check out the other Remote Development extensions.
Set Up Ssh Server Linux Mint
Or get them all by installing the Remote Development Extension Pack.
